
If you want to make a smart choice regarding solar energy, you need to know “solar panel wattage vs. size.” The link between solar panel size and electricity output is defined by this principle. For homeowners, RV owners, and businesses alike, understanding this balance helps maximize efficiency, reduce costs, and make the most of available space.
Introduction to Solar Panel Wattage and Size
Solar panel wattage directly influences how much power a panel can produce. Higher wattage panels are often larger but offer significant energy returns, making them suitable for homes with large power needs or commercial buildings. However, for smaller spaces, such as RVs or homes with limited roof space, lower wattage options may be more practical despite producing less power overall.
Why Solar Panel Wattage vs. Size Matters
Maximizing Efficiency for Energy Needs
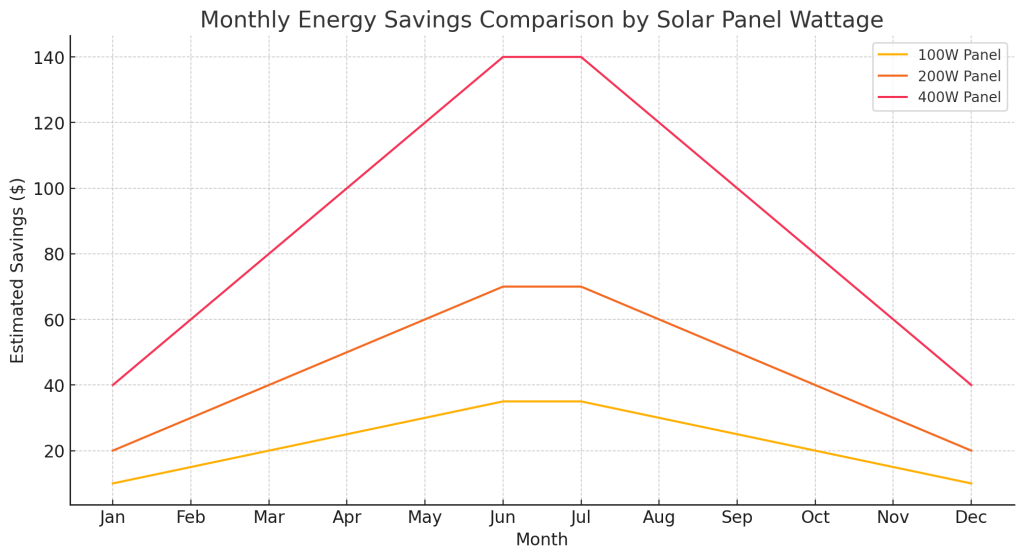
Efficiency, size, and wattage affect solar panel performance in real life. Efficiency is the proportion of sunlight a solar panel can convert into energy. Higher efficiency equals more energy in less area. This metric is crucial because:
- Space efficiency: Limited roof space means selecting panels with a higher watt per square foot.
- Cost-effectiveness: Higher efficiency panels can reduce the overall number of panels required, saving money on both material and installation.
Advantages of Higher Solar Panel Wattage
Higher wattage panels provide several benefits, especially for homeowners with higher power demands. Let’s explore these advantages.
- More Power Generation: Higher wattage panels can generate more power per panel, ideal for households with high electricity usage.
- Reduced Installation Costs: Fewer panels are needed, meaning less labor and fewer mounting materials.
- Better for Limited Space: When roof space is limited, high-wattage panels allow you to make the most of each square foot.
Best Solar Panel Size for a Small Roof
If you have a smaller roof, balancing wattage and dimensions becomes crucial. Solar panels designed specifically for compact areas can still offer impressive solar panel output without taking up too much space. This efficiency makes these panels great for small homes or specific roof sections where maximizing each square foot is a priority.
Disadvantages of Higher Solar Panel Wattage
While there are notable advantages to higher wattage, some downsides must also be considered.
- Higher Cost: High-wattage panels tend to be pricier per panel, which may impact the initial investment.
- Increased Weight: These panels are often larger and heavier, potentially stressing some roof structures.
- Limited Flexibility: If more panels are needed later, matching the wattage may be challenging if technology or availability changes.
Types of Solar Panels and Their Wattage
There are several types of solar panels available, each suited for different purposes:
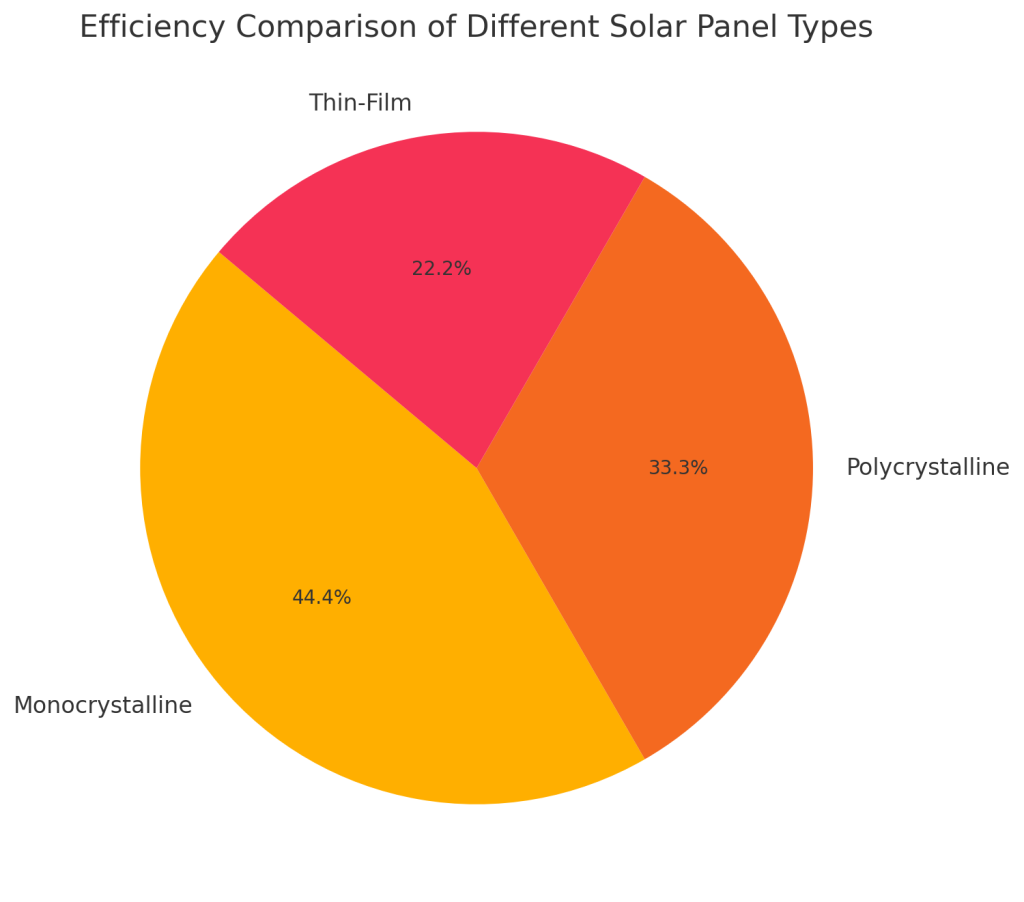
- Monocrystalline Panels: Known for high efficiency and durability, these panels offer a high wattage per square foot and are ideal for homes with limited roof space.
- Polycrystalline Panels: Slightly less efficient but more affordable, these are ideal for larger installations where space isn’t an issue.
- Thin-Film Panels: Highly flexible and lightweight, thin-film panels are less efficient per square foot, making them suitable for expansive, low-wattage installations.
Each of these types has unique solar panel power rating characteristics, impacting which type might be best suited for your needs.
Solar Panel Size and Wattage Comparisons
Comparing Solar Panel Sizes by Use
Solar panels are available in a range of sizes to suit different applications. Here’s a quick comparison:
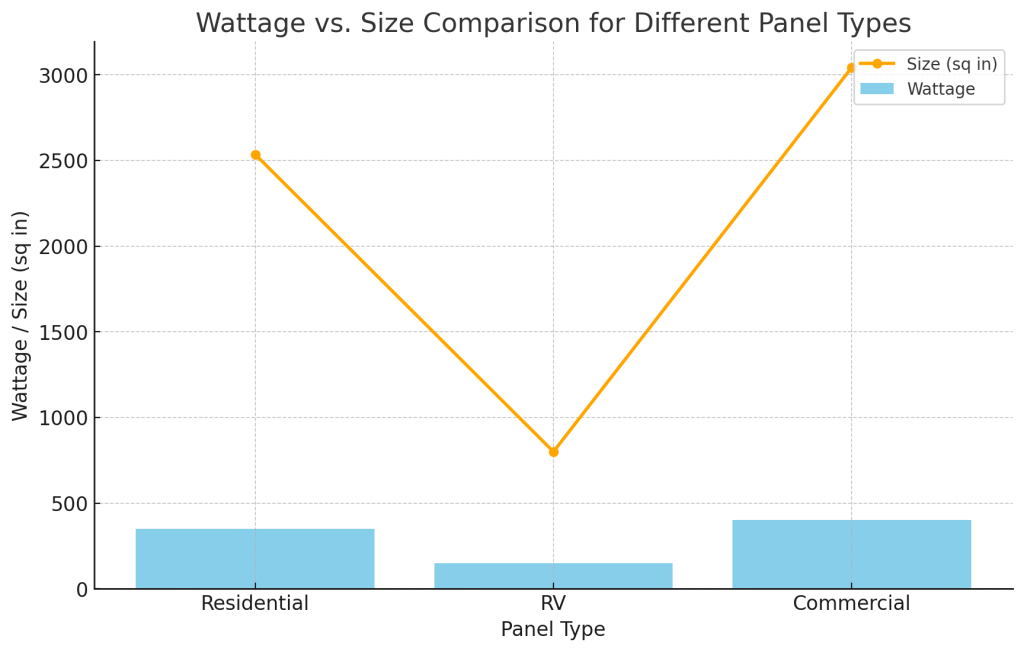
- Home Installations: Standard panels for home use are typically around 65 inches by 39 inches, with wattages between 250 and 400 watts.
- Small Roofs and RVs: Smaller panels for tight spaces or RVs come in dimensions like 40 inches by 20 inches with wattages of around 100-200 watts.
- Large Commercial Use: Large panels for commercial installations can exceed 78 inches in length and produce upwards of 400 watts.
Solar Panel Dimensions in Inches for Common Sizes
- 2×4 Frame Panels: Panels designed for compact setups, such as RVs, often measure around 24 inches by 48 inches.
- Full-Size Panels: For residential use, typical panels measure approximately 65 by 39 inches.

Knowing the solar panel dimensions helps tailor an installation that maximizes both energy output and space utilization.
Color Variations in Solar Panels
The color of a solar panel, typically either black or blue, can impact its efficiency, aesthetics, and sometimes cost. Here’s a closer look at how color affects these aspects:
1. Efficiency
- Black Solar Panels (Monocrystalline): These panels are usually made from high-purity silicon and are known for their higher efficiency. Silicon absorbs light, making it black and allowing it to collect more sunlight even on overcast days or early morning/evening hours. This makes black panels a great choice for maximizing energy output on limited roof space.
- Blue Solar Panels (Polycrystalline): Blue panels use polycrystalline silicon, which is less pure and less efficient than black panels. The blue tint originates from an anti-reflective coating that captures light, although not as well as black panels. Their reduced efficiency can be offset by adding panels to homes with sufficient of roof space, making them an affordable option.
2. Aesthetics
- Black Panels: Due to their uniform, sleek appearance, black panels are often considered more visually appealing, especially for residential homes. They tend to blend in better with dark roofs and can offer a more modern, streamlined look. For homeowners prioritizing curb appeal, black panels are often the preferred choice.
- Blue Panels: These panels have a distinctive blue sheen that’s sometimes seen as less aesthetically pleasing compared to black panels. However, some homeowners find the blue look unique, and on certain roof types or with specific building designs, blue panels can still look attractive.
3. Temperature Sensitivity
- Both black and blue panels may work in hot weather, although black panels absorb more heat due to their hue. This can, in rare cases, lead to slight efficiency losses on extremely hot days. However, manufacturers design panels to tolerate high temperatures, so for most regions, the color difference has minimal impact on performance due to temperature.
- Blue panels can sometimes stay a bit cooler since they absorb less light, which might marginally improve performance in very hot climates. However, this difference is usually minimal and often not a deciding factor.
4. Cost
- Black Panels (Monocrystalline) tend to be more expensive because they’re made from high-purity silicon, which requires more resources and energy to produce. This cost may be balanced by their higher efficiency, especially if the installation area is limited.
- Blue Panels (Polycrystalline) are generally more affordable, which can make them appealing for larger installations or those looking to save on initial costs.
Summary: Choosing Based on Color
Blue (Polycrystalline): Ideal for those with larger space, seeking a budget-friendly option, or where aesthetics are less of a priority.
Black (Monocrystalline): Best for those with limited space, needing high efficiency, or desiring a sleek, modern look.
Calculating Solar Panel Size for Homes and Small Spaces
Using a solar panel size calculator can simplify determining the right panel dimensions for your specific needs. By entering details like roof area, power usage, and sun exposure, these calculators provide a tailored recommendation on the number and size of panels required.
For instance, homeowners with small roofs might find a mix of high-efficiency panels is ideal, while those with larger spaces might focus on cost-effective panels with lower watt per square foot ratings.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Lasting Solar Panels
Solar panels require minimal maintenance but taking steps to keep them in peak condition can boost their lifespan and efficiency. Here are a few essential tips:
- Regular Cleaning: Dust and debris can lower solar panel output. Cleaning panels once every three to six months can keep them operating at full capacity.
- Annual Inspections: Checking for wear, wiring issues, or loose connections each year ensures safe, efficient energy production.
- Monitor Performance: Using a performance tracker can alert you to any drops in output, allowing for timely maintenance.
FAQs on Solar Panel Wattage and Size
What is the best solar panel size for a small roof?
For smaller roofs, high-efficiency panels in compact sizes (e.g., 40×20 inches) work well, allowing maximum output without occupying excessive space.
How do I calculate solar panel size and wattage for my home?
A solar panel size calculator helps determine the best configuration by inputting factors like available roof area, desired power output, and daily sunlight exposure.
Are black solar panels more efficient than blue ones?
Yes, generally, black monocrystalline panels are more efficient in direct sunlight compared to blue polycrystalline panels, though they may be slightly more expensive.
How many watts do I need for an RV solar setup?
RV solar setups typically use panels between 100 to 200 watts each, with the total wattage depending on energy needs and available mounting space.
What factors affect solar panel efficiency?
Solar panel efficiency is affected by factors like solar panel dimensions, type, and watt per square foot, as well as sun exposure and cleanliness.
Is it worth installing higher wattage panels?
Higher wattage panels are a good investment when space is limited or energy needs are high, as they offer more power per square foot and can reduce overall installation costs.
Conclusion
Get a feel for how “solar panel wattage vs. size” connects to your power needs, space limitations, and budget before making a final decision. Whether you have a small roof, an RV, or a commercial property, finding the right balance of wattage and size can ensure an efficient, cost-effective, and reliable solar power system tailored just for you.